Flink – window operator
参考,
http://wuchong.me/blog/2016/05/25/flink-internals-window-mechanism/
http://wuchong.me/blog/2016/06/06/flink-internals-session-window/
WindowOperator
window operator通过WindowAssigner和Trigger来实现它的逻辑
当一个element到达时,通过KeySelector先assign一个key,并且通过WindowAssigner assign若干个windows,这样这个element会被放入若干个pane
一个pane会存放所有相同key和相同window的elements
/**<br/>
* An operator that implements the logic for windowing based on a {@link WindowAssigner} and<br/>
* {@link Trigger}.<br/>
*<br/>
* <p><br/>
* When an element arrives it gets assigned a key using a {@link KeySelector} and it gets<br/>
* assigned to zero or more windows using a {@link WindowAssigner}. Based on this, the element<br/>
* is put into panes. A pane is the bucket of elements that have the same key and same<br/>
* {@code Window}. An element can be in multiple panes if it was assigned to multiple windows by the<br/>
* {@code WindowAssigner}.<br/>
*<br/>
* <p><br/>
* Each pane gets its own instance of the provided {@code Trigger}. This trigger determines when<br/>
* the contents of the pane should be processed to emit results. When a trigger fires,<br/>
* the given {@link InternalWindowFunction} is invoked to produce the results that are emitted for<br/>
* the pane to which the {@code Trigger} belongs.<br/>
*<br/>
* @param <K> The type of key returned by the {@code KeySelector}.<br/>
* @param <IN> The type of the incoming elements.<br/>
* @param <OUT> The type of elements emitted by the {@code InternalWindowFunction}.<br/>
* @param <W> The type of {@code Window} that the {@code WindowAssigner} assigns.<br/>
*/<br/>
@Internal<br/>
public class WindowOperator<K, IN, ACC, OUT, W extends Window><br/>
extends AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, InternalWindowFunction<ACC, OUT, K, W>><br/>
implements OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT>, Triggerable, InputTypeConfigurable {
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------<br/>
// Configuration values and user functions<br/>
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
protected final WindowAssigner<? super IN, W> windowAssigner;
protected final KeySelector<IN, K> keySelector;
protected final Trigger<? super IN, ? super W> trigger;
protected final StateDescriptor<? extends AppendingState<IN, ACC>, ?> windowStateDescriptor;
/**<br/>
* The allowed lateness for elements. This is used for:<br/>
* <ul><br/>
* <li>Deciding if an element should be dropped from a window due to lateness.<br/>
* <li>Clearing the state of a window if the system time passes the<br/>
* {@code window.maxTimestamp + allowedLateness} landmark.<br/>
* </ul><br/>
*/<br/>
protected final long allowedLateness; //允许late多久,即当watermark已经触发后
/**<br/>
* To keep track of the current watermark so that we can immediately fire if a trigger<br/>
* registers an event time callback for a timestamp that lies in the past.<br/>
*/<br/>
protected transient long currentWatermark = Long.MIN_VALUE;
protected transient Context context = new Context(null, null); //Trigger Context
protected transient WindowAssigner.WindowAssignerContext windowAssignerContext; //只为获取getCurrentProcessingTime
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------<br/>
// State that needs to be checkpointed<br/>
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**<br/>
* Processing time timers that are currently in-flight.<br/>
*/<br/>
protected transient PriorityQueue<Timer<K, W>> processingTimeTimersQueue; //Timer用于存储timestamp,key,window, queue按时间排序
/**<br/>
* Current waiting watermark callbacks.<br/>
*/<br/>
protected transient Set<Timer<K, W>> watermarkTimers;<br/>
protected transient PriorityQueue<Timer<K, W>> watermarkTimersQueue; //
protected transient Map<K, MergingWindowSet<W>> mergingWindowsByKey; //用于记录merge后的stateWindow和window的对应关系
对于window operator而已,最关键的是WindowAssigner和Trigger
WindowAssigner
WindowAssigner,用于指定一个tuple应该被分配到那些windows去
借用个图,可以看出有多少种WindowAssigner
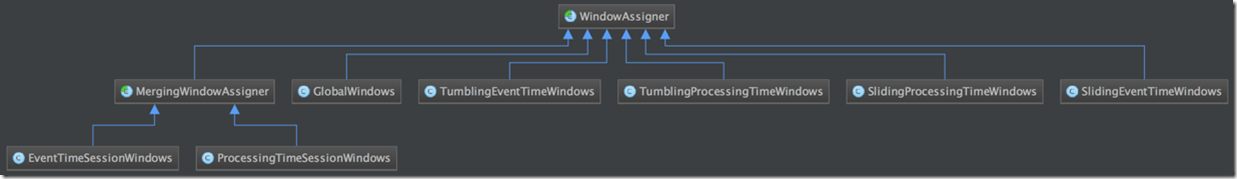
对于WindowAssigner,最关键的接口是,assignWindows
为一个element,分配一组windows, Collection<W>
@PublicEvolving<br/>
public abstract class WindowAssigner<T, W extends Window> implements Serializable {<br/>
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**<br/>
* Returns a {@code Collection} of windows that should be assigned to the element.<br/>
*<br/>
* @param element The element to which windows should be assigned.<br/>
* @param timestamp The timestamp of the element.<br/>
* @param context The {@link WindowAssignerContext} in which the assigner operates.<br/>
*/<br/>
public abstract Collection<W> assignWindows(T element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context);
/**<br/>
* Returns the default trigger associated with this {@code WindowAssigner}.<br/>
*/<br/>
public abstract Trigger<T, W> getDefaultTrigger(StreamExecutionEnvironment env);
/**<br/>
* Returns a {@link TypeSerializer} for serializing windows that are assigned by<br/>
* this {@code WindowAssigner}.<br/>
*/<br/>
public abstract TypeSerializer<W> getWindowSerializer(ExecutionConfig executionConfig);
实际看下,具体WindowAssigner的实现
public class TumblingProcessingTimeWindows extends WindowAssigner<Object, TimeWindow> {
@Override<br/>
public Collection<TimeWindow> assignWindows(Object element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context) {<br/>
final long now = context.getCurrentProcessingTime();<br/>
long start = now - (now % size);<br/>
return Collections.singletonList(new TimeWindow(start, start + size)); //很简单,分配一个TimeWindow<br/>
}
@Override<br/>
public Trigger<Object, TimeWindow> getDefaultTrigger(StreamExecutionEnvironment env) {<br/>
return ProcessingTimeTrigger.create(); //默认给出的是ProcessingTimeTrigger,如其名<br/>
}
public class SlidingEventTimeWindows extends WindowAssigner<Object, TimeWindow> {
private final long size;<br/>
private final long slide;
@Override<br/>
public Collection<TimeWindow> assignWindows(Object element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context) {<br/>
if (timestamp > Long.MIN_VALUE) {<br/>
List<TimeWindow> windows = new ArrayList<>((int) (size / slide));<br/>
long lastStart = timestamp - timestamp % slide;<br/>
for (long start = lastStart;<br/>
start > timestamp - size;<br/>
start -= slide) {<br/>
windows.add(new TimeWindow(start, start + size)); //可以看到这里会assign多个TimeWindow,因为是slide<br/>
}<br/>
return windows;<br/>
} else {
}<br/>
}
@Override<br/>
public Trigger<Object, TimeWindow> getDefaultTrigger(StreamExecutionEnvironment env) {<br/>
return EventTimeTrigger.create();<br/>
}
Trigger, Evictor
下面看看3个主要的接口,分别触发,onElement,onEventTime,onProcessingTime
processElement
处理element到达的逻辑,触发onElement
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {<br/>
Collection<W> elementWindows = windowAssigner.assignWindows( //通过WindowAssigner为element分配一系列windows<br/>
element.getValue(), element.getTimestamp(), windowAssignerContext);
final K key = (K) getStateBackend().getCurrentKey();
if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) { //如果是MergingWindow<br/>
//.......<br/>
} else { //如果是普通window<br/>
for (W window: elementWindows) {
// drop if the window is already late<br/>
if (isLate(window)) { //late data的处理,默认是丢弃<br/>
continue;<br/>
}
AppendingState<IN, ACC> windowState = getPartitionedState( //从backend中取出该window的状态,就是buffer的element<br/>
window, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);<br/>
windowState.add(element.getValue()); //把当前的element加入buffer state
context.key = key;<br/>
context.window = window; //context的设计相当tricky和晦涩
TriggerResult triggerResult = context.onElement(element); //触发onElment,得到triggerResult
if (triggerResult.isFire()) { //对triggerResult做各种处理<br/>
ACC contents = windowState.get();<br/>
if (contents == null) {<br/>
continue;<br/>
}<br/>
fire(window, contents); //如果fire,真正去计算窗口中的elements<br/>
}
if (triggerResult.isPurge()) {<br/>
cleanup(window, windowState, null); //purge,即去cleanup elements<br/>
} else {<br/>
registerCleanupTimer(window);<br/>
}<br/>
}<br/>
}<br/>
}
判断是否是late data的逻辑
protected boolean isLate(W window) {<br/>
return (windowAssigner.isEventTime() && (cleanupTime(window) <= currentWatermark));<br/>
}<br/>
private long cleanupTime(W window) {<br/>
long cleanupTime = window.maxTimestamp() + allowedLateness; //allowedLateness;<br/>
return cleanupTime >= window.maxTimestamp() ? cleanupTime : Long.MAX_VALUE;<br/>
}
fire逻辑
private void fire(W window, ACC contents) throws Exception {<br/>
timestampedCollector.setAbsoluteTimestamp(window.maxTimestamp());<br/>
userFunction.apply(context.key, context.window, contents, timestampedCollector);<br/>
}
processWatermark
处理watermark,onEvent触发
@Override<br/>
public void processWatermark(Watermark mark) throws Exception {<br/>
boolean fire;<br/>
do {<br/>
Timer<K, W> timer = watermarkTimersQueue.peek(); //这叫watermarkTimersQueue,是否有些歧义,叫eventTimerQueue更好理解些<br/>
if (timer != null && timer.timestamp <= mark.getTimestamp()) {<br/>
fire = true;
watermarkTimers.remove(timer);<br/>
watermarkTimersQueue.remove();
context.key = timer.key;<br/>
context.window = timer.window;<br/>
setKeyContext(timer.key); //stateBackend.setCurrentKey(key);
AppendingState<IN, ACC> windowState;<br/>
MergingWindowSet<W> mergingWindows = null;
if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) { //MergingWindow<br/>
mergingWindows = getMergingWindowSet();<br/>
W stateWindow = mergingWindows.getStateWindow(context.window);<br/>
if (stateWindow == null) {<br/>
// then the window is already purged and this is a cleanup<br/>
// timer set due to allowed lateness that has nothing to clean,<br/>
// so it is safe to just ignore<br/>
continue;<br/>
}<br/>
windowState = getPartitionedState(stateWindow, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);<br/>
} else { //普通window<br/>
windowState = getPartitionedState(context.window, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor); //取得window的state<br/>
}
ACC contents = windowState.get();<br/>
if (contents == null) {<br/>
// if we have no state, there is nothing to do<br/>
continue;<br/>
}
TriggerResult triggerResult = context.onEventTime(timer.timestamp); //触发onEvent<br/>
if (triggerResult.isFire()) {<br/>
fire(context.window, contents);<br/>
}
if (triggerResult.isPurge() || (windowAssigner.isEventTime() && isCleanupTime(context.window, timer.timestamp))) {<br/>
cleanup(context.window, windowState, mergingWindows);<br/>
}
} else {<br/>
fire = false;<br/>
}<br/>
} while (fire); //如果fire为true,继续看下个waterMarkTimer是否需要fire
output.emitWatermark(mark); //把waterMark传递下去
this.currentWatermark = mark.getTimestamp(); //更新currentWaterMark<br/>
}
trigger
首先,这个函数的命名有问题,为何和前面的process…不匹配
这个是用来触发onProcessingTime,这个需要依赖系统时间的定时器来触发,逻辑和processWatermark基本等同,只是触发条件不一样
@Override<br/>
public void trigger(long time) throws Exception {<br/>
boolean fire;
//Remove information about the triggering task<br/>
processingTimeTimerFutures.remove(time);<br/>
processingTimeTimerTimestamps.remove(time, processingTimeTimerTimestamps.count(time));
do {<br/>
Timer<K, W> timer = processingTimeTimersQueue.peek();<br/>
if (timer != null && timer.timestamp <= time) {<br/>
fire = true;
processingTimeTimers.remove(timer);<br/>
processingTimeTimersQueue.remove();
context.key = timer.key;<br/>
context.window = timer.window;<br/>
setKeyContext(timer.key);
AppendingState<IN, ACC> windowState;<br/>
MergingWindowSet<W> mergingWindows = null;
if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) {<br/>
mergingWindows = getMergingWindowSet();<br/>
W stateWindow = mergingWindows.getStateWindow(context.window);<br/>
if (stateWindow == null) {<br/>
// then the window is already purged and this is a cleanup<br/>
// timer set due to allowed lateness that has nothing to clean,<br/>
// so it is safe to just ignore<br/>
continue;<br/>
}<br/>
windowState = getPartitionedState(stateWindow, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);<br/>
} else {<br/>
windowState = getPartitionedState(context.window, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);<br/>
}
ACC contents = windowState.get();<br/>
if (contents == null) {<br/>
// if we have no state, there is nothing to do<br/>
continue;<br/>
}
TriggerResult triggerResult = context.onProcessingTime(timer.timestamp);<br/>
if (triggerResult.isFire()) {<br/>
fire(context.window, contents);<br/>
}
if (triggerResult.isPurge() || (!windowAssigner.isEventTime() && isCleanupTime(context.window, timer.timestamp))) {<br/>
cleanup(context.window, windowState, mergingWindows);<br/>
}
} else {<br/>
fire = false;<br/>
}<br/>
} while (fire);<br/>
}
EvictingWindowOperator
Evicting对于WindowOperator而言,就是多了Evictor
private void fire(W window, Iterable<StreamRecord<IN>> contents) throws Exception {<br/>
timestampedCollector.setAbsoluteTimestamp(window.maxTimestamp());
// Work around type system restrictions...<br/>
int toEvict = evictor.evict((Iterable) contents, Iterables.size(contents), context.window); //执行evict
FluentIterable<IN> projectedContents = FluentIterable<br/>
.from(contents)<br/>
.skip(toEvict)<br/>
.transform(new Function<StreamRecord<IN>, IN>() {<br/>
@Override<br/>
public IN apply(StreamRecord<IN> input) {<br/>
return input.getValue();<br/>
}<br/>
});<br/>
userFunction.apply(context.key, context.window, projectedContents, timestampedCollector);<br/>
}
转发申明:
本文转自互联网,由小站整理并发布,在于分享相关技术和知识。版权归原作者所有,如有侵权,请联系本站 top8488@163.com,将在24小时内删除。谢谢




